

No light enters the eye from the shadow of the object.ģ. Image is seen when light coming from the object after reflection or refraction enters the observes’s eye.Ģ. Shadow is formed when light falls on the opaque body.Ģ. Image is formed due to reflection or refraction of lightġ.
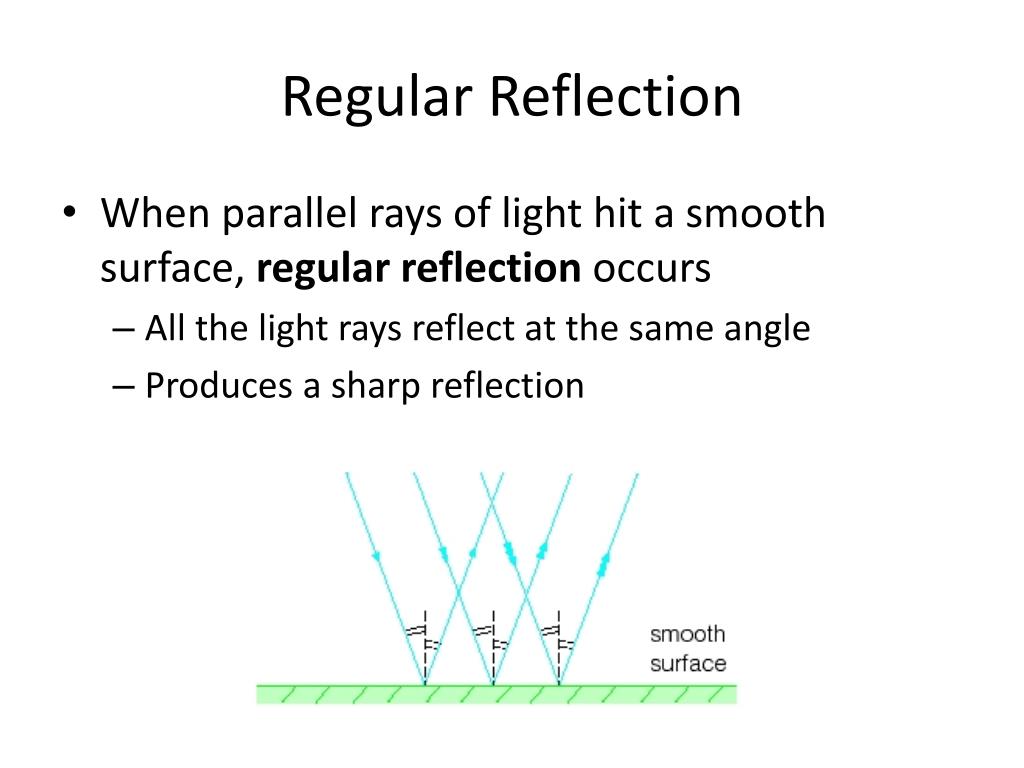
What is the difference between image and shadow?ġ. The colour of the opaque object does not affect the colour of the shadow that is formed. On this screen is a dark patch, or shadow, with the same outline as the object surrounded by light. The wall or ground behind the opaque object is the screen. Everywhere else around the opaque object, the light continues in a straight path until it bounces off the ground or wall behind the object. It is formed when light hits the opaque object which does not let the light pass through. What is a shadow? How is it formed? How does the colour of an opaque object affect the colour of the shadow?Ī shadow is a dark outline or image cast by an opaque object that blocks light coming from a source of light. The length of the shadow also changes from season to season. Yes, the direction of shadow changes as the sun changes its position during the day. an opaque object in the way of light, andĭoes the direction of shadow change during the day? Does the length of shadow also change from season to season?.What do we need in order to see a shadow? All the space behind the opaque object up to some distance behind it seems to be filled with the shadow Shadow is not just the two-dimensional outline that you see on the ground. Whether a shadow is two-dimensional or three-dimensional? Wood and bricks are the substances through which light does not pass. Give examples of two substances through which light does not pass? On what factor does the proportion of light that enters an object depend?Īn object which comes to the path of light is called an obstacle. Write down four man-made sources of light.

The objects which emit light of their own are called luminous bodies, e.g., the sun, the stars, etc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
